
Over ‘129,000 looking death in the eyes’ in South Sudan, Somalia – UN says
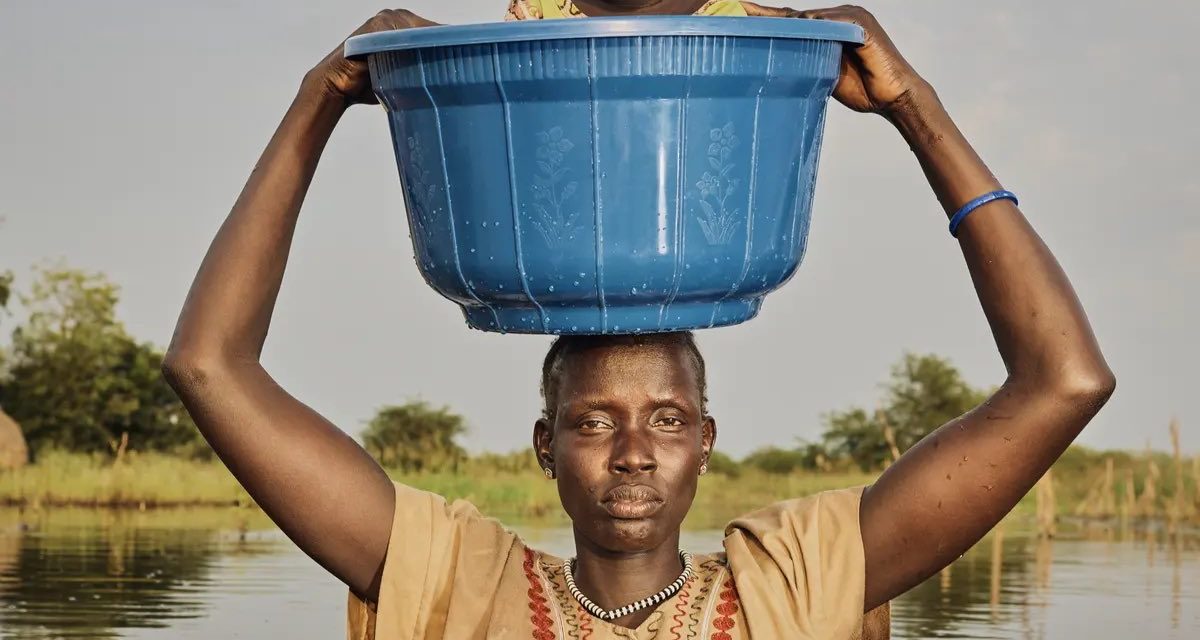

Cover Photo Credit: Peter Caton for Action Against Hunger
First Published by UN News on 10 March 2023
Life-threatening hunger caused by climate shocks, violent insecurity, and disease in the Horn of Africa, have left nearly 130,000 people “looking death in the eyes” and nearly 50 million facing crisis levels of food insecurity, the UN World Health Organization (WHO) said last week.
In an appeal for $178 million to support humanitarian assistance across the seven affected countries in the Greater Horn region, veteran WHO worker Liesbeth Aelbrecht warned that the situation was worse than anything she’d seen in more than two decades in Djibouti, Ethiopia, Kenya, Somalia, South Sudan, Sudan, and Uganda.
“These 48 million people do include as many as 129,000 who are facing catastrophe; and catastrophe, that means they are facing starvation and literally looking death in the eyes,” Ms. Aelbrecht told journalists in Geneva. Those most at risk, are living in both South Sudan and Somalia.
On Wednesday, the World Food Programme’s Regional Director for East Africa, Michael Dunford wrote on twitter about South Sudan’s worsening Climate crises siting draught, hunger and floods as the indicators.
In addition to the dramatic hunger crisis, the region has never seen such a high number of reported disease outbreaks this century, according to WHO.
“All seven countries are battling measles, a deadly disease,” Ms. Aelbrecht said, stating that people suffering from malnutrition are much more vulnerable to sickness than those who have enough to eat.
“Four of the countries are fighting cholera, South Sudan being one of them; they just declared an outbreak. Malaria, which we know is endemic in this region and remains the biggest cause reason for (medical) consultation, is really on the rise.”
The Greater Horn region is also in the grip of concurrent outbreaks of hepatitis, meningitis and dengue, which was declared for the first time in Khartoum in February.
“The frequency of these disease outbreaks is directly linked to these extreme weather events and to climate change,” the WHO officer said. “I’ve been working on and off in this region for almost 25 years now – and in terms of accumulated emergencies, this is bad as I’ve ever seen it.”
In response to the emergency, the UN health agency intends to use its $178 million appeal to scale up treatment of people suffering from medical complications linked to severe malnutrition.
The WHO appeal will also help ensure that the health system does not collapse by providing mobile health clinics, as increasingly desperate pastoral communities leave their homes and arrive in towns.
“We need to do anything possible to control these disease outbreaks,” said Ms. Aelbrecht. “We know how to control cholera, what we need is really the resources to scale this up.”



















Recent Comments